
As blockchain technology evolves, interoperability has become essential to the ecosystem’s success. Polkadot’s parachain infrastructure allows for interoperability amongst different blockchain networks, and XCM (Cross-Chain Message) is the standardized messaging protocol that enables cross-chain communication.
In this article, we will explore the crucial role of XCM in Bifrost’s Liquid Staking Protocol and the recent upgrades in XCM v3 that have improved the speed and security Bifrost’s liquidity protocol.
Why is XCM important for Parachains?
Polkadot Wiki explains this problem:
“One of Polkadot’s main functionalities is interoperability amongst parachains and any other participating consensus-driven systems. XCM is the language through which complex, cross-consensus interactions can occur. Two blockchains can “speak” XCM to seamlessly interact with each other using a standard messaging format.”- Polkadot Wiki Learn XCM
Parachains utilize a standardized messaging protocol, which allows for explicit and secure communication between chains, akin to Morse code. This communication format ensures mutual understanding while maintaining the accuracy and security of cross-chain information transmission.
Why is XCM important for Bifrost?
Bifrost is a multi-chain liquid staking protocol that must communicate with other chains to perform operations such as staking, unstaking, switching validator/collator, and receiving execution messages back from those chains. Bifrost uses this method to ensure the original staked token reserves each liquid staking derivative.
Therefore, the logic above mainly relates to two operations using XCM:
Sending assets and messages to a destination chain. Retrieving messages from a destination chain. XCM V1-V2 mainly defined how to send messages, while the upgrade of XCM v3 adds message query functionality:query_respond.
Including the message query feature simplifies Bifrost’s ability to verify the message status sent to the other chain, streamlining the communication process.
What protocol features did Bifrost upgrade using XCM v3?
SALP - MultiSig Confirmation Service Removed
SALP (Slot Auction Liquidity Protocol) is the underlying runtime module of Liquid Crowdloans. It provides liquid crowdloan tokens for crowdloan contributors. To learn more about SALP, click here.
XCM V2 requires a multisig server to serve as a relayer between Bifrost and Polkadot, enabling the teleportation of event results. The server must inform Bifrost of the success or failure of the contribution, ensuring that the contribution fund reserves the liquid crowdloan token.
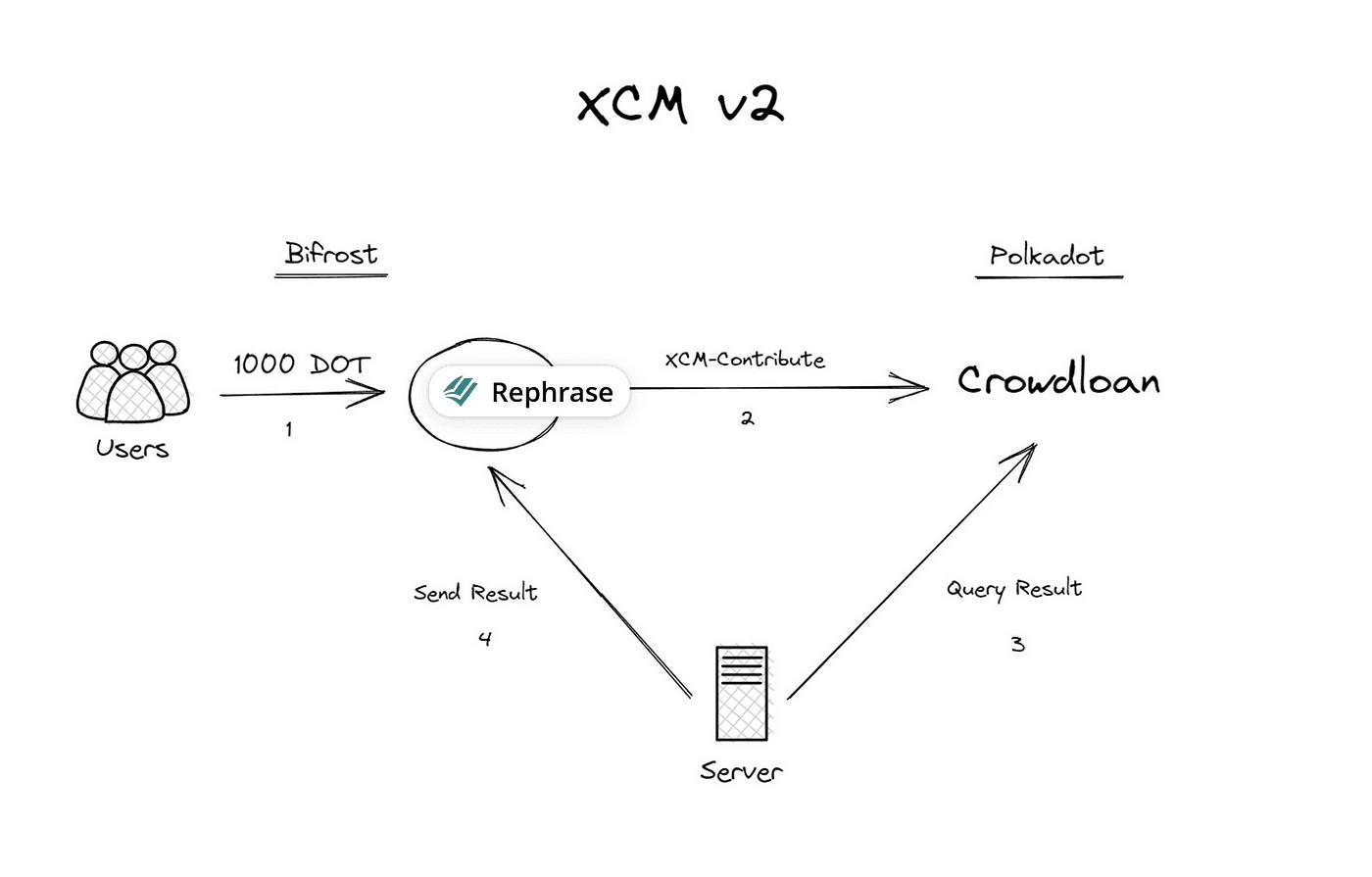
However, upgrading to XCM v3 eliminates the need for a multisig server. Instead, the XCM v3 query response replaces it, enabling Bifrost SALP to query Polkadot with a simple Yes or No answer.
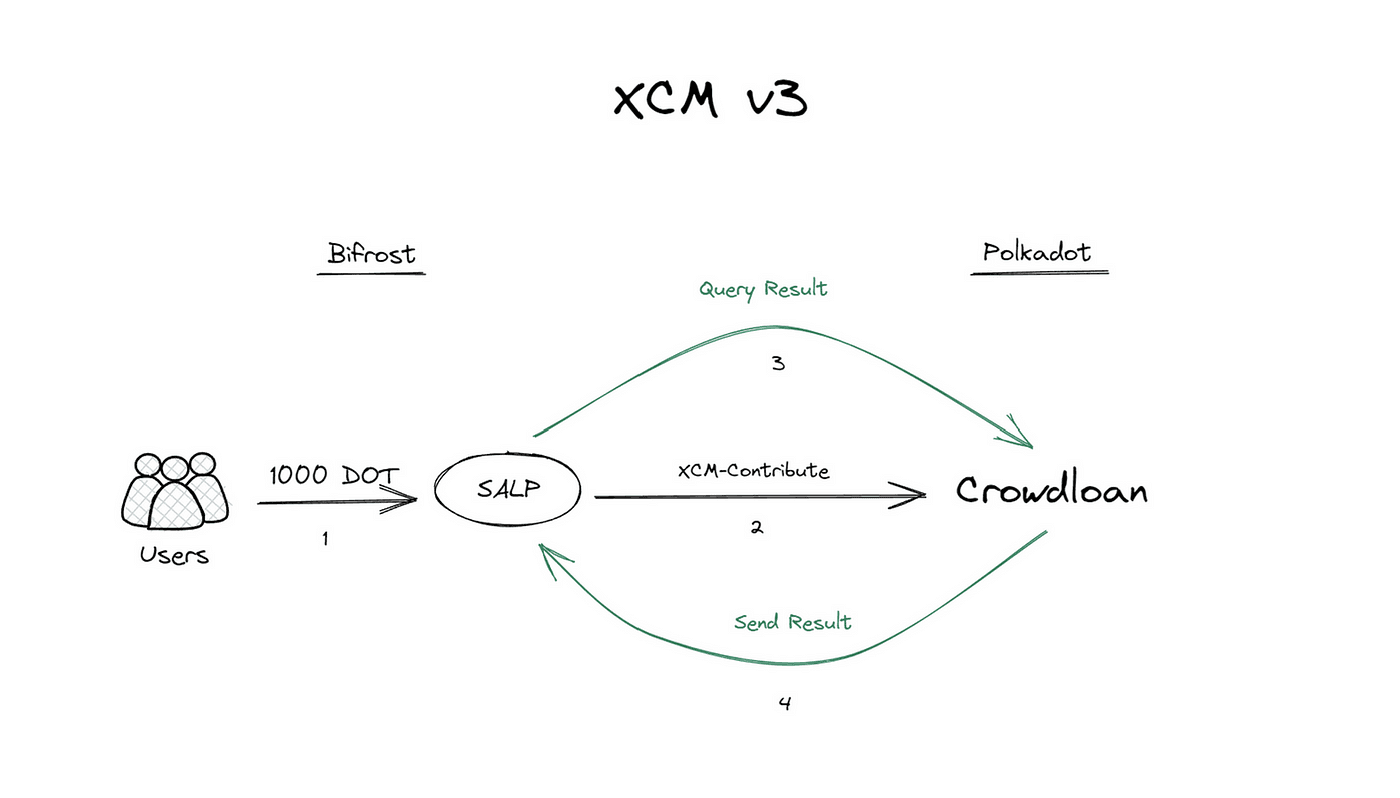
SLP - Message Confirmation Upgrade
Bifrost’s Staking Liquidity Protocol (SLP) utilizes a message-synchronized flow, which is more complex than the SALP approach. To learn more about SLP, click here. The price appreciated model of their liquid staking tokens needs regular monitoring to make accurate price adjustments. Find out more about this process in the Bifrost doc.
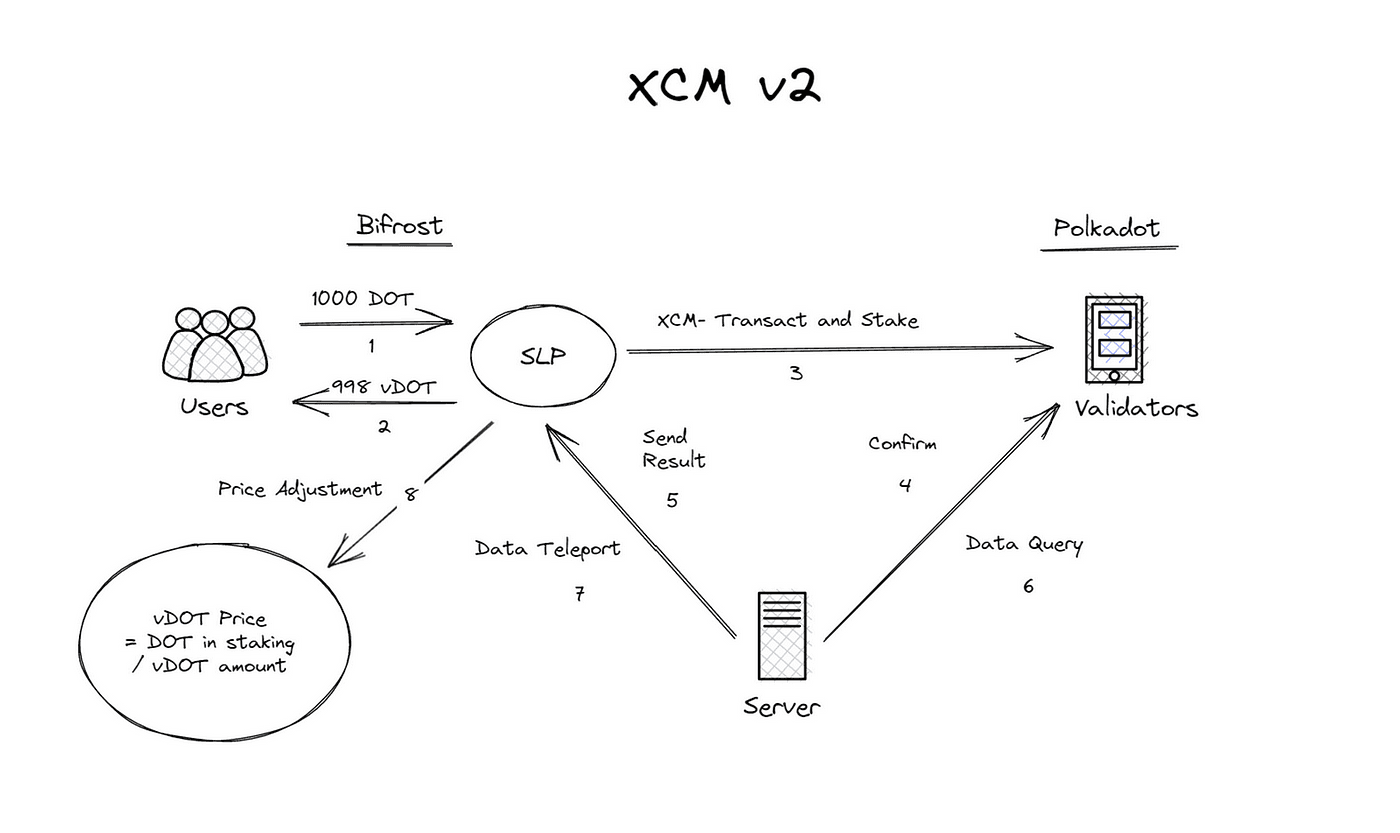
XCM Action - Transaction Confirmation
XCM Action pallet simplifies vToken minting with a cross-chain function, enabling users to expand the application of vToken liquidity to different chains. It also supports convenient swaps and liquidation for a broader application range.
The underlying logic of the XCM action allows users to initiate vToken minting on a target chain. Bifrost’s XCM action pallet simplifies asset transactions for users. It automatically transfers the asset to its platform, mints a vToken and then returns it to the target chain in an easy-to-manage form. Thus, the user does not need to bring their asset to Bifrost themselves.
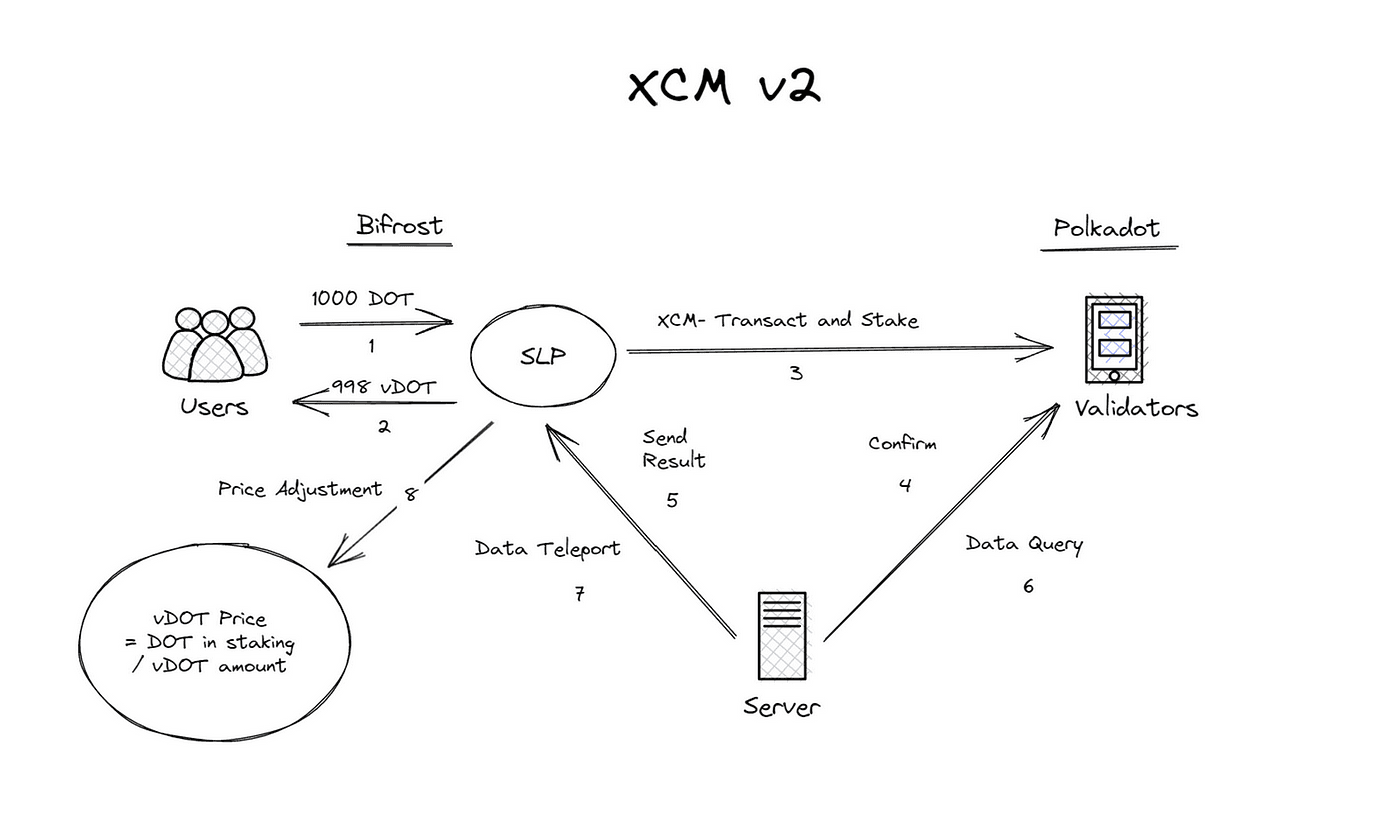
XCM v3 upgrades empower the action pallet to ensure all transaction details throughout the workflow are accessible and accurately confirmed.
How Does XCM v3 Benefit Users?
The evolution of XCM mainly improves the speed and security of the Bifrost product. Users can receive vsTokens faster than ever and check their XCM transaction results under validated transactions rather than through a relayer.
Furthermore, XCM v3 enables more potential use cases between parachains, although, at this point, it only queries results. The Bifrost product will soon become more decentralized with the addition of upcoming features, such as the ability to query data from a pallet.



