 2022 / 08 / 25 14:00
2022 / 08 / 25 14:00 Bifrost
Bifrost
The focus of the chain in the third quarter of this year was undoubtedly the auction of Kusama slots. Through two rounds of auctions, 11 candidates were awarded slots in a fierce competition to become the Kusama Parachain. Bifrost also received slots in the first round of slot auctions and supported the other candidates with SALP in the second round of slot auctions.
Polkadot officials announced that they will open a slot auction on Polkadot’s Mainnet on November 11. Bifrost is ready to deploy SALP services on Polkadot to support bidding for more projects.
Parachain bidding is a model unique to Polkadot. Polkadot is essentially a multi-chain architecture with a slice mechanism that gives Parachains shared security by allowing relay chain verifiers to verify Parachain blocks. However, there is a limit to the number of Parachains that a relay chain can access. In order to allocate the limited Parachain slots to more valuable Parachains, Polkadot/Kusama will use an auction for each Parachain project to compete for slot leases. The competition is done by staking DOT/KSM to the relay chain, and the more stakes, the more likely it will get slots. This process is known as Slot Aution.
Parachains can raise DOT/KSM from their respective communities by means of Crowdloan when bidding for slots, and DOT/KSM holders can choose to contribute their DOT/KSM to any bidding project they like. However, in this process, Crowdloan participants inevitably lose the liquidity of their DOT/KSM holdings.

SALP Slot Auction Liquidity Protocol aims to release the liquidity of DOT/KSM locked in the Parachain auction process for the Polakdot ecosystem by issuing derivative assets anchored to locked assets. For Crowdloan participants, staking KSM/DOT while obtaining derivatives that can be readily liquidated improves capital utilization; for Parachains bidding for slots, SALP attracts more contributors who do not want to lose opportunity costs and increases the probability of successful bidding.
Review: SALP on Kusama SALP protocol was official launched on September 16, 2021 and supports Bifrost in the second round of slot auctions with four other Parachains.
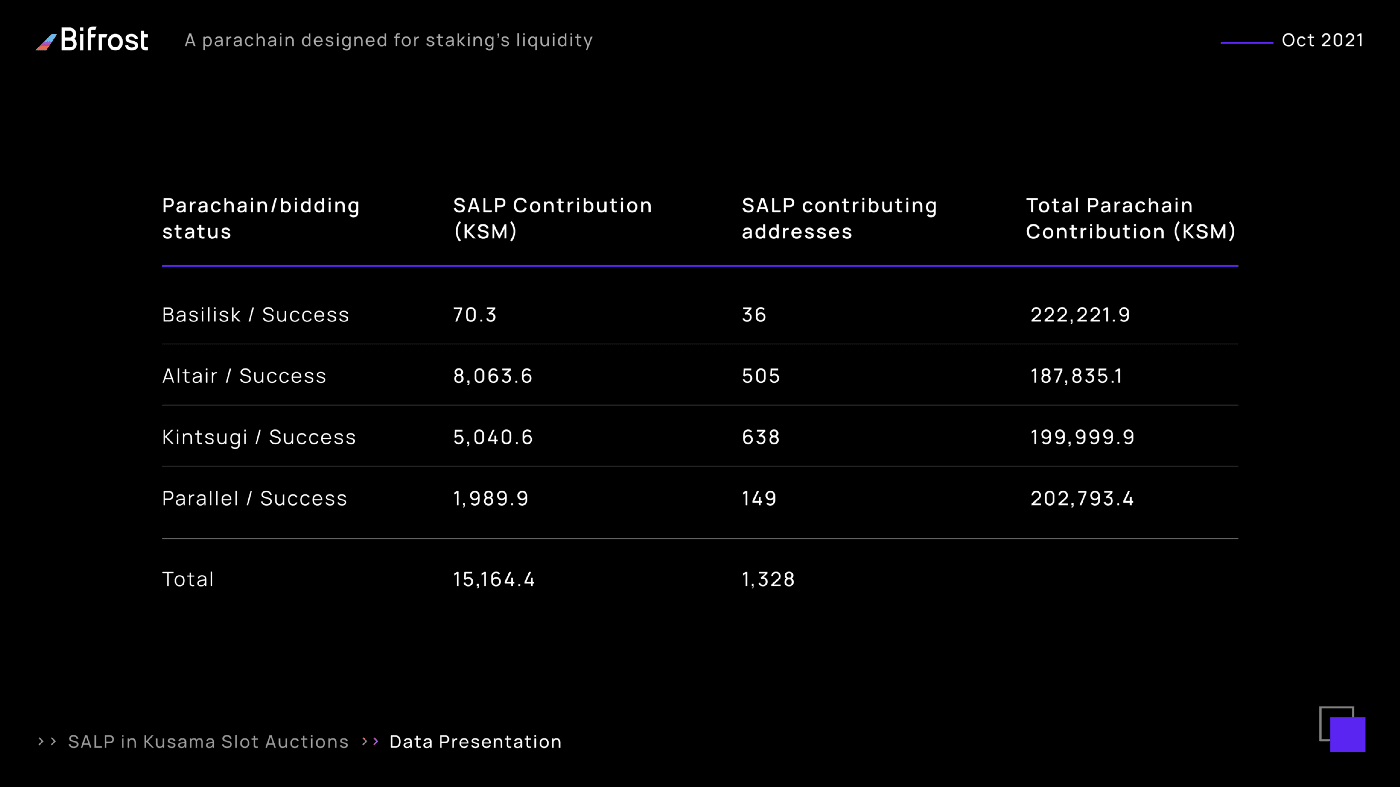
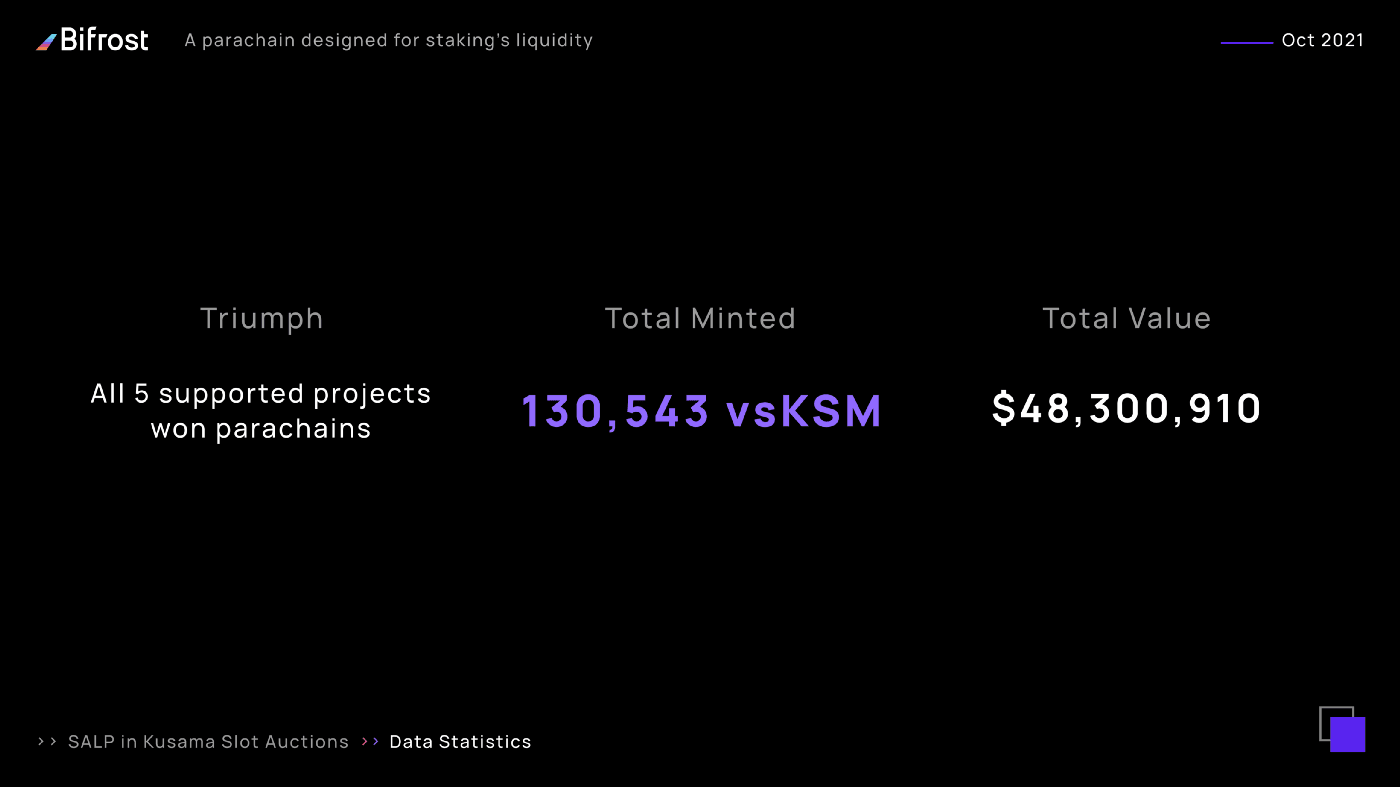
In the second round of Kusama slot bidding, the SALP minted 15,164.4 vsKSM & vsBond for Altair, Kintsugi, Parallel and Basilisk, with a cumulative value of over 54,712,944.
Migration: SALP on Polkadot The implementation of SALP on Kusama is divided into two phases, a multi-signature model before Bifrost becomes a Kusama Parachain and an XCM model after Bifrost becomes a Kusama Parachain, where the former requires trust that the multi-signature group is honest and the latter is implemented through pure on-chain logic with no trust assumptions.
SALP on Polkadot will also go through two phases.
Phase 1: Multi-signature
Before Bifrost became a Polkadot Parachain, the Polkadot relay chain, managed by a team of Witnesses, multi-signed accounts to collect contributions and notify the Bifrost chain to mint derivatives for users, which was done because the Polkadot and Kusama ecosystems were not interconnected and Polkadot messages could not be passed through XCM to the Bifrost chain as a Kusama Parachain Bifrost chain, which is a Parachain to Kusama.
The Mint process is as follows:
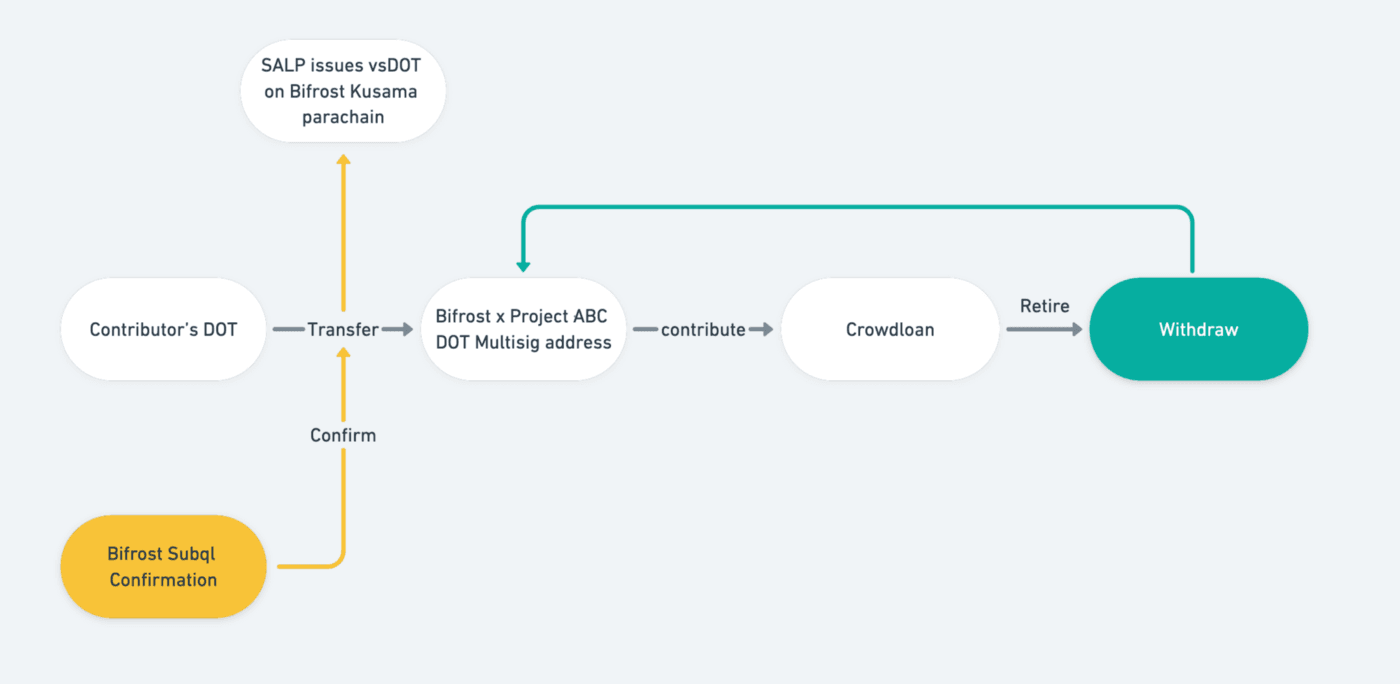
- All user-contributed DOTs will be transferred to the multi-signature address created by Bifrost on the Polkadot side.
- Bifrost’s Subql multi-signature validation service will verify that the transfer of DOTs to the multi-signature address is successful.
- Initiated by Bifrost, the multi-signer confirms and performs a multi-signer and contributes the DOT from the multi-signer address to Polkadot Crowdloan.
- The Bifrost side mints derivatives for the user: vsDOT and vsBond.
The Redeem process is as follows:
There are two scenarios, the failed bid and the expiration of the Parachain lease.
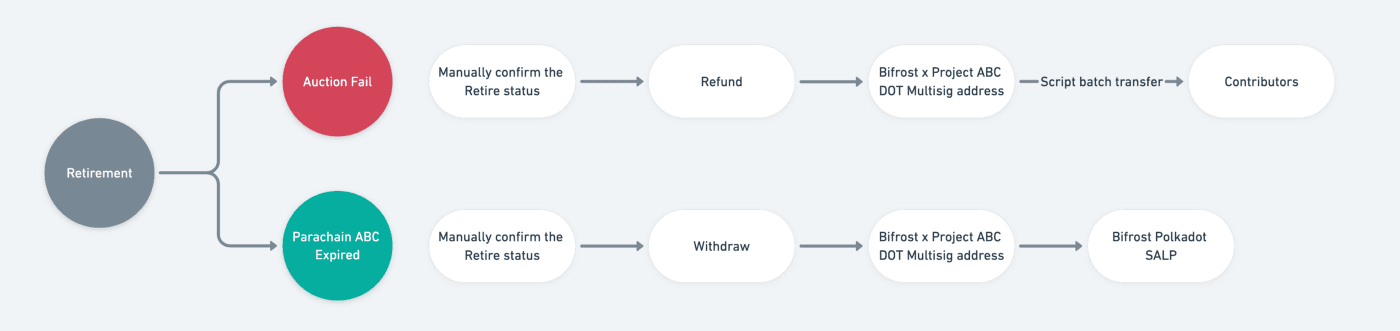
The bidding failed and the crowdloan ended
- The multisigner manually confirms the ‘Retireable’ status of the crowdloan
- Execute the ‘Retire’ and Polkadot returns the DOT to the Bifrost multi-signer address
- Multisigner performs a bulk transfer and returns the DOT to the user.
Auction successful, Parachain lease expires
- The multisigner manually confirms the ‘Retireable’ status of the crowdloan
- Execute end of retirement, Polkadot returns DOT to Bifrost multi-signer address
- Multisigner performs a bulk transfer of DOT to Bifrost SALP (Polkadot Parachain) and the user completes the DOT acceptance with vsDOT + vsBond.
Phase 2: XCM (de-trusting)
After Bifrost became a Polkadot Parachain, Bifrost wanted to achieve the same complete de-trusting as SALP on Kusama, where the entire process is executed through on-chain logic.
But after Bifrost became Polkadot Parachain, there was another factor that governed the shift from multi-signature to de-trusting.
The XCM protocol consists of two parts, a UMP responsible for passing messages from the Parachain to the relay chain and a DMP responsible for passing messages from the relay chain to the Parachain. The version of XCM on Polkadot, unlike the version of XCM on Kusama, only supports the UMP and not yet the DMP. this results in a situation where after a user contribute, the Bifrost chain cannot learn its status and issue derivatives.
So before Polkadot supported DMP, SALP could only implement part of the on-chain logic, and although multi-signature accounts were no longer needed, the multi-signature team was still required to perform the DMP work on behalf of the Bifrost chain, responsible for confirming and passing the state on the relay chain. The process is as follows.
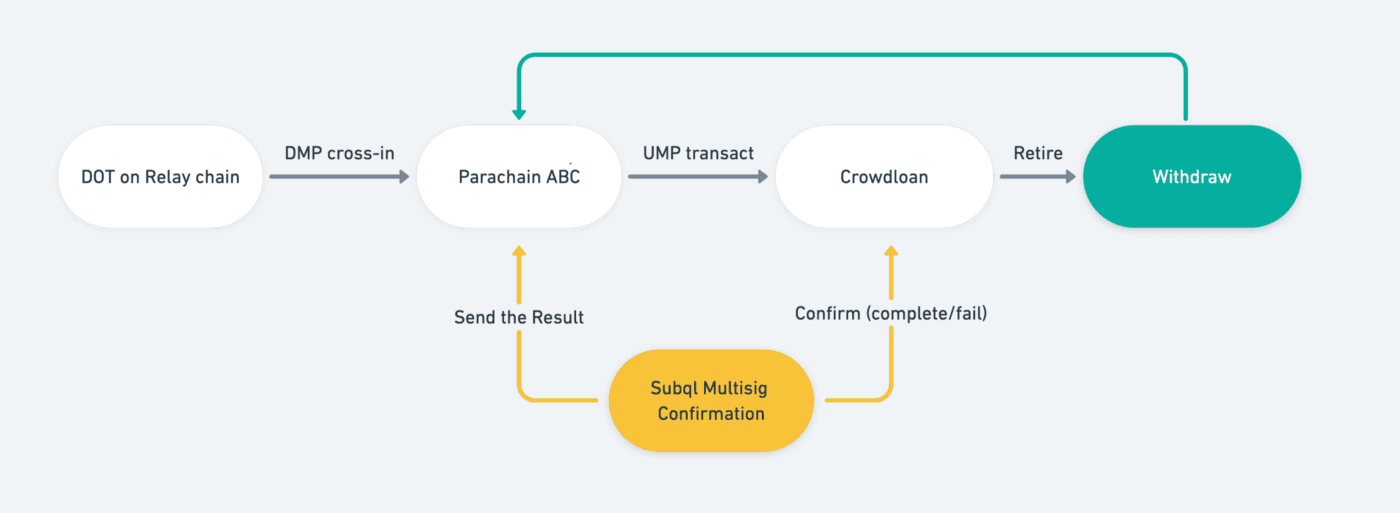
When Polkadot’s XCM version supports DMP, multi-signature confirmation services will no longer be needed and a pure on-chain logical, de-trusted SALP will be implemented.
In conclusion, during the development of SALP on Polkadot, Bifrost will take a step-by-step approach with the strategy of implementing the core functions as soon as possible and gradually moving towards de-trusting to provide a secure and decentralized liquidity release service for more Parachain candidates and users participating in Crowdloan.
What is Bifrost?
Bifrost is the Polkadot Ecological DeFi basic protocol. It is committed to becoming an infrastructure for staked assets to provide liquidity. Bifrost launched derivatives vToken for Staking and Polkadot Parachain Slot (Crowdloan). It has obtained $2.15M in fund-raising from NGC, SNZ, DFG, CMS and other institutions and Web3 Foundation Grant. It is also a member of Substrate Builders Program and Web3 Bootcamp.
vToken can optimize transactions in multiple scenarios such as DeFi, DApp, DEX, CEX, and realize the transfer channel of stake rights such as staking and Crowdloan through vToken, realize the risk hedging of stake assets, and expand scenarios such as vToken as collateral for lending, its staking reward part of the interest can be offset to achieve low-interest loans.
